English III 2021
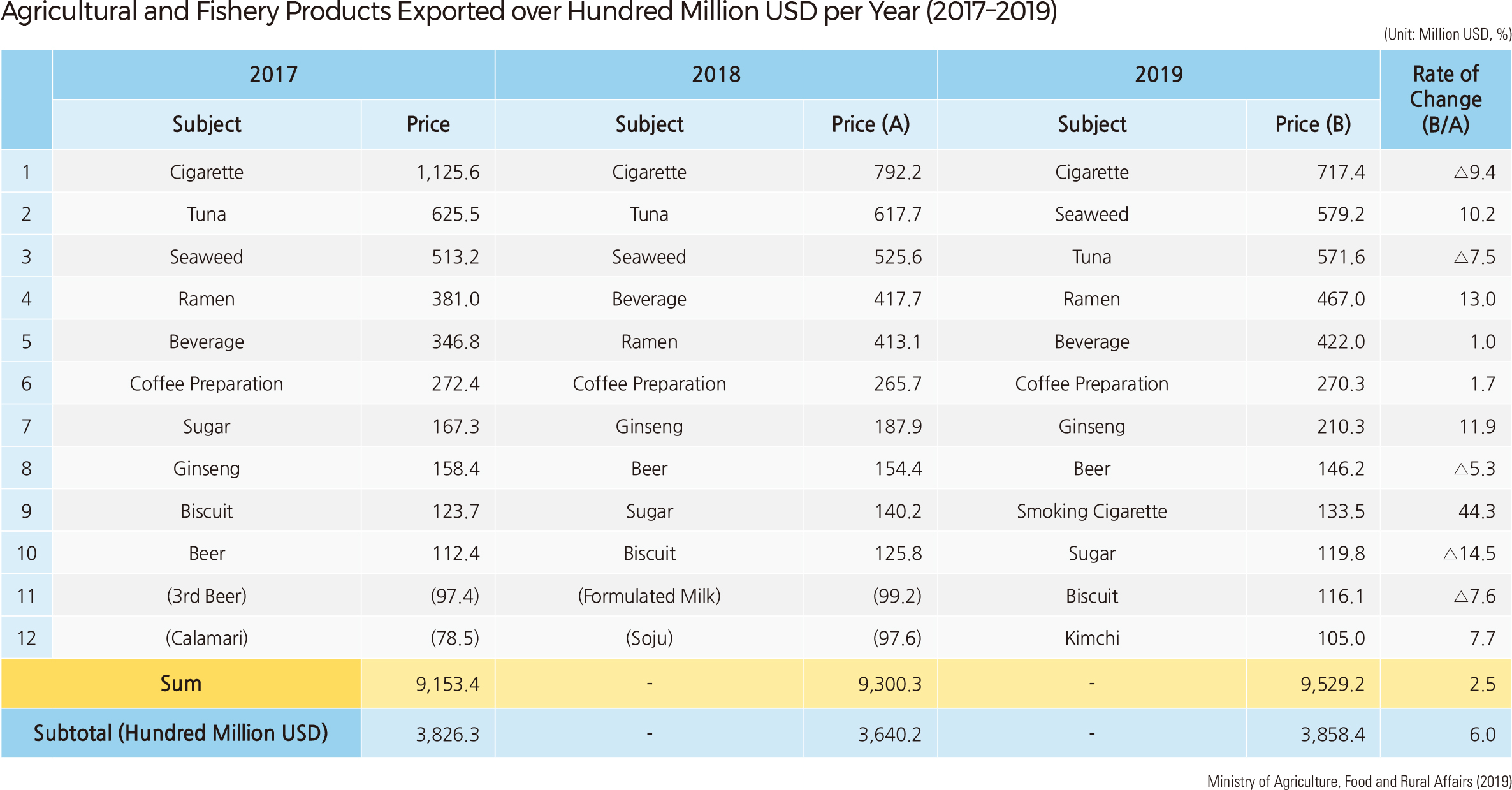
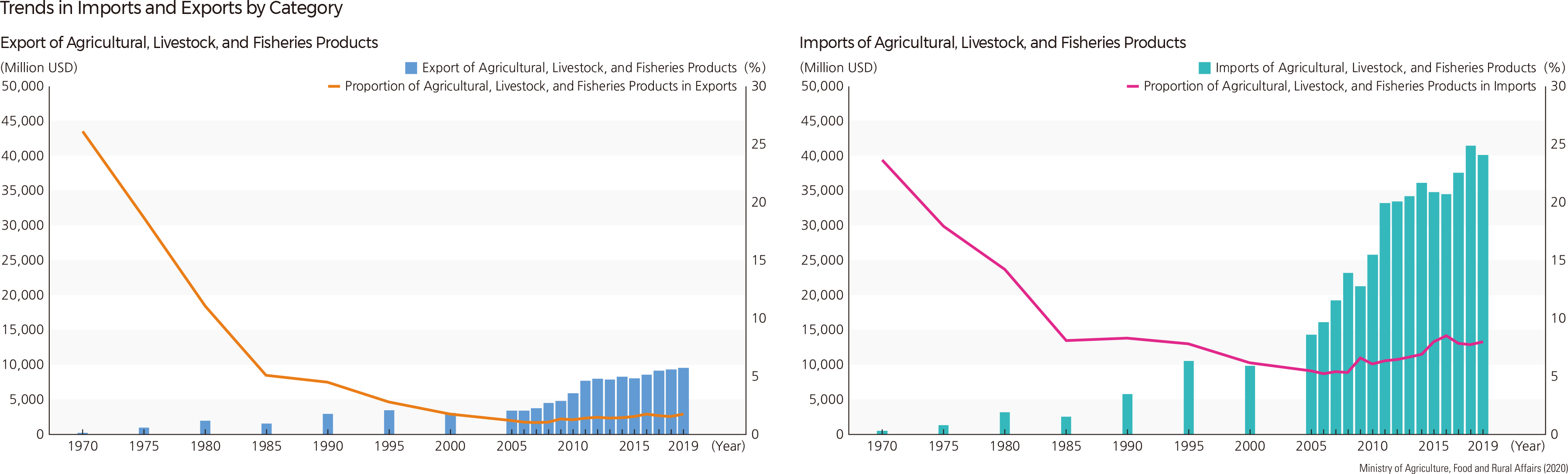
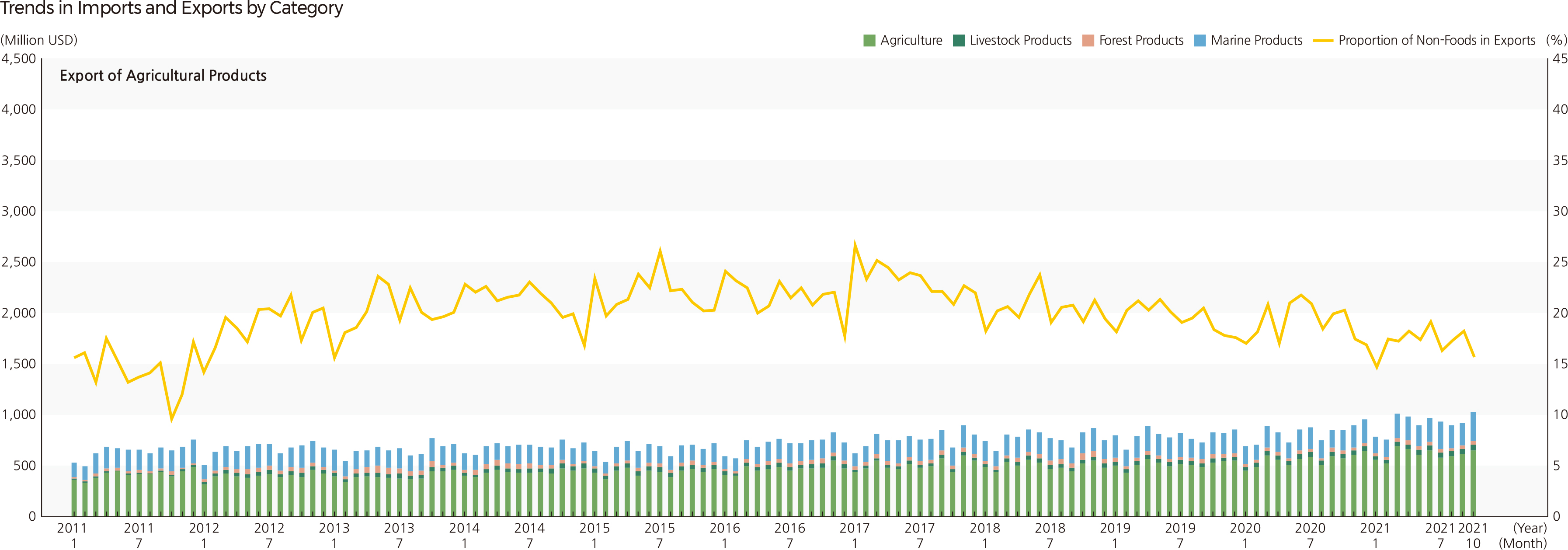
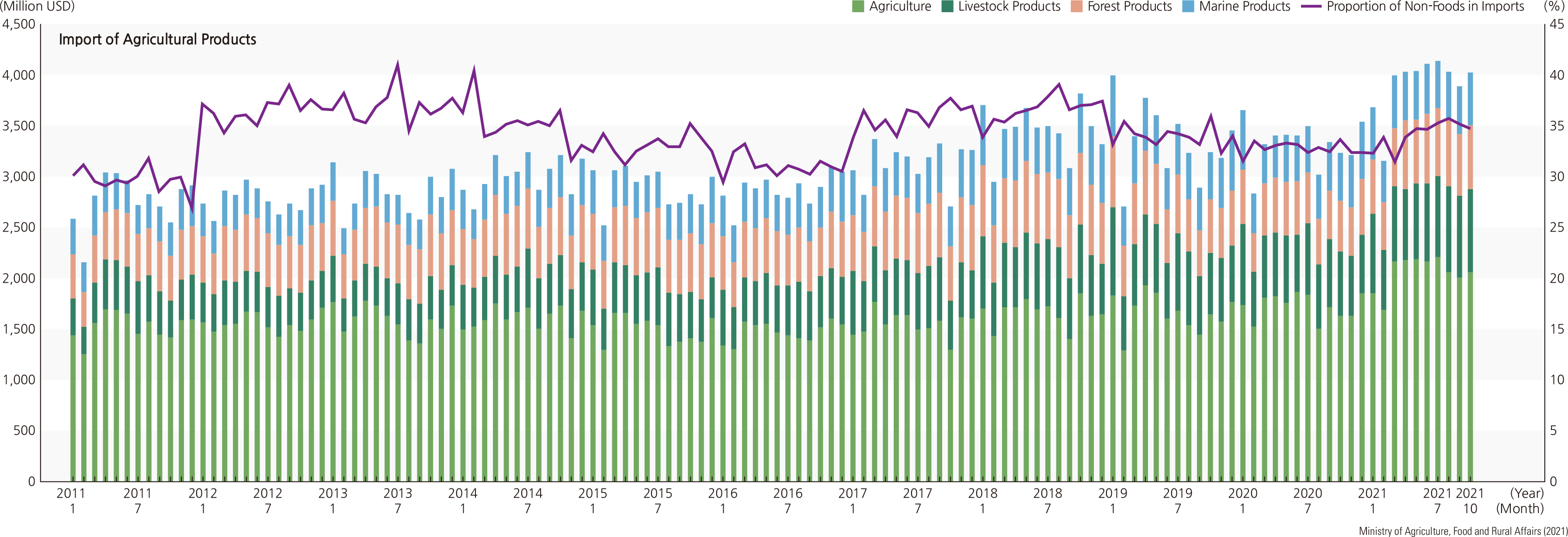
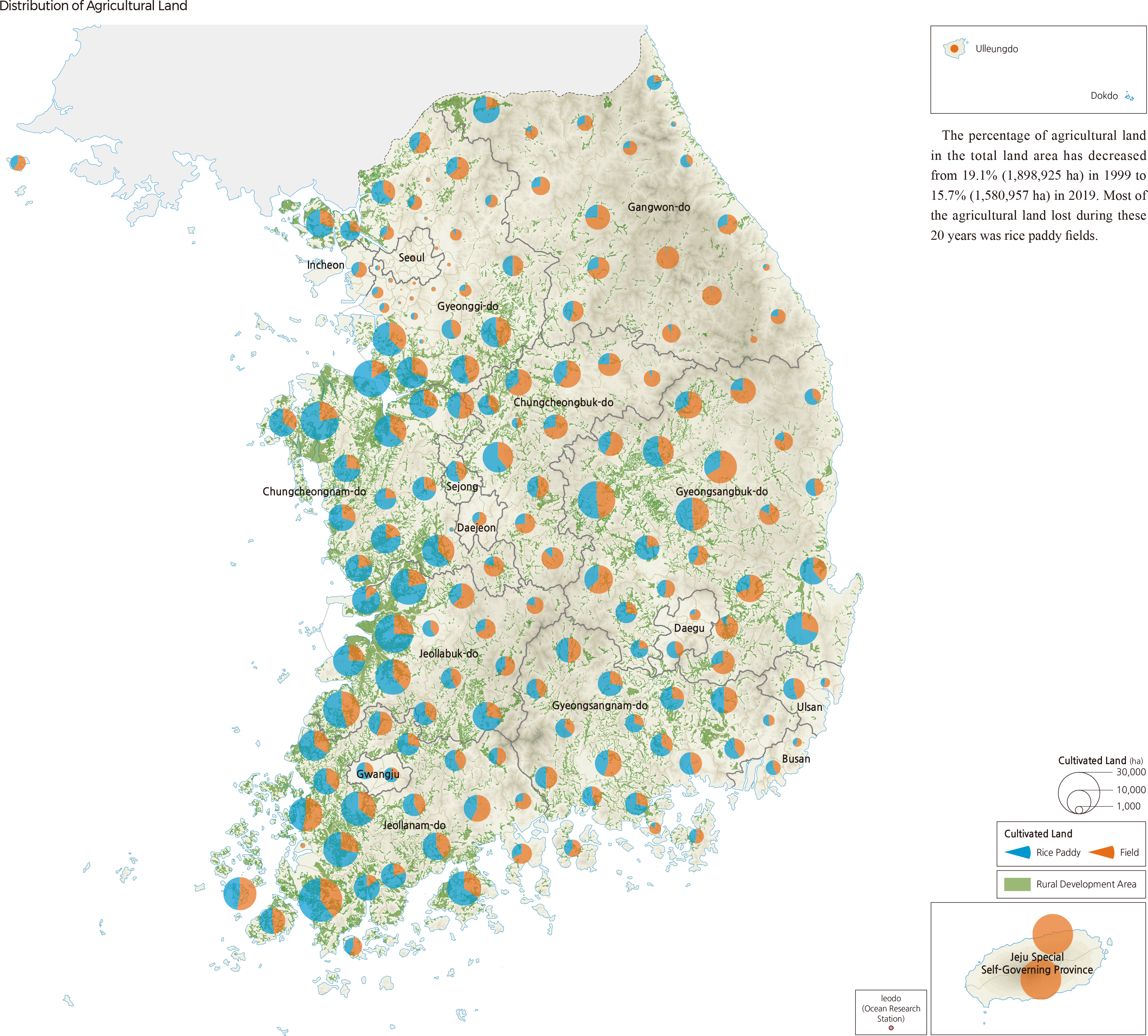
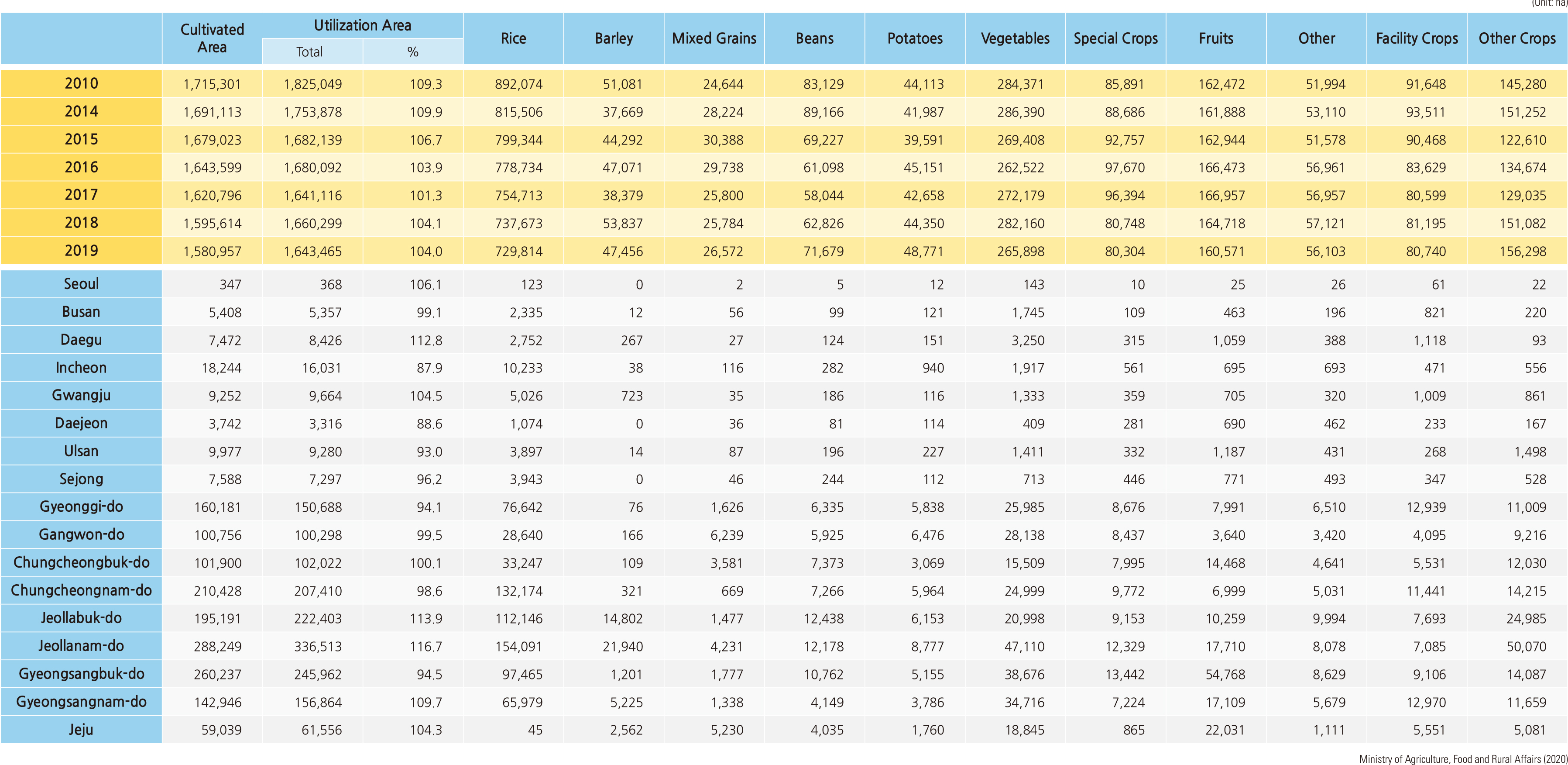
Korea’s agricultural and fishery product imports increased 4.1 times from $9.86 billion in 2000 to $40.09 billion in 2019, and its exports increased by 3.1 times from $3.04 billion to $9.53 billion. As can be seen from the huge trade deficit in agricultural and fishery products, Korea’s food self-sufficiency rate decreased from 69.6% in 1980 to 45.8% in 2019. Since 2001, the government has set the “major food self-sufficiency target” to secure food security. As of 2020, most agricultural and fishery products are close to the target, but grain products, including wheat (7.1%), corn (8.5%), and soybeans (13.9%), were far short of the target. The self-sufficiency rate of animal products decreased sharply: beef from 53.6% in 1990 to 36.3% in 2018, pork, chicken, and seafood from over 100% in 1990 to 71.6%, 89.9%, and 51.2% in 2018, respectively. In 2019, imports of agricultural products were 19.9 billion USD. Imports of grains increased, while imports of vegetables and fruits decreased. Imports of livestock products have increased, while imports of forest and aquatic products are on the decline. Imports of favorite products, such as coffee and wine, have increased. The percentage of agricultural land in the total land area has decreased from 19.1% (1,898,925 ha) in 1999 to 15.7% (1,580,957 ha) in 2019. Most of the agricultural land lost during these 20 years was rice paddy fields. |